Introduction
Monetary policy is the engine driving global economies, influencing everything from inflation rates to the value of your investment portfolio. But what exactly is monetary policy, and how does it affect your financial decisions? Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the U.S., the European Central Bank (ECB), and the Bank of Japan, use tools like interest rates, quantitative easing, and forward guidance to steer economic growth, stabilize prices, and manage employment. For investors, understanding these policies is critical to navigating market volatility and seizing opportunities. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll demystify monetary policy, explore its impact on stocks, bonds, real estate, and currencies, and provide actionable strategies to protect and grow your wealth. Whether you’re new to investing or a seasoned professional, this post will equip you with the knowledge to thrive in any economic environment.
What Is Monetary Policy?
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by central banks to manage a country’s money supply and interest rates, aiming to achieve macroeconomic goals like price stability, full employment, and sustainable growth. Unlike fiscal policy, which involves government spending and taxation (see our post on Fiscal Policy Explained), monetary policy is controlled by independent institutions like the Federal Reserve or the ECB. These institutions operate with varying degrees of autonomy, a topic we explore in Federal Reserve Independence at Risk?.
The primary objectives of monetary policy are:
- Price Stability: Keeping inflation low and predictable, often targeting 2% annually, as seen with the Fed and ECB.
- Full Employment: Supporting job creation by stimulating or cooling economic activity.
- Economic Growth: Promoting steady GDP growth without triggering overheating or recessions.
For investors, monetary policy is a critical driver of market performance. A single rate hike or policy shift can ripple through asset classes, affecting returns on stocks, bonds, and real estate. In 2025, these dynamics are particularly relevant, as outlined in our Global Economic Outlook 2025.
Central Bank Tools and Their Effects
Central banks wield a sophisticated set of tools to influence economies. Here’s a detailed look at the main instruments and their impacts:
- Interest Rates: The cornerstone of monetary policy. Raising rates increases borrowing costs, slowing economic activity and curbing inflation. Lowering rates encourages borrowing and investment, stimulating growth. For example, the Fed’s 2022–2023 rate hikes to combat 7% inflation reduced stock valuations but stabilized prices.
- Open Market Operations (OMOs): Central banks buy or sell government bonds to adjust the money supply. Buying bonds injects cash, boosting liquidity; selling bonds withdraws cash, tightening conditions. The Bank of Japan’s bond purchases in 2020 supported markets during the pandemic.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): In crises, central banks purchase large-scale assets (e.g., bonds, mortgage-backed securities) to flood the economy with liquidity. The Fed’s $1.7 trillion QE program post-2008 financial crisis is a landmark example, stabilizing markets but inflating asset prices.
- Forward Guidance: Central banks communicate future policy intentions to shape market expectations. For instance, the ECB’s 2019 commitment to low rates reassured investors, supporting bond markets. The BIS supports central bank coordination to align global monetary policies, enhancing their collective impact.
These tools interact with global economic trends, as explored in our Global Economic Outlook 2025. Understanding them helps investors anticipate market shifts.
How Monetary Policy Impacts Investments
Monetary policy directly influences the performance of major asset classes. Here’s a breakdown of its effects, with historical data to illustrate:
Stocks
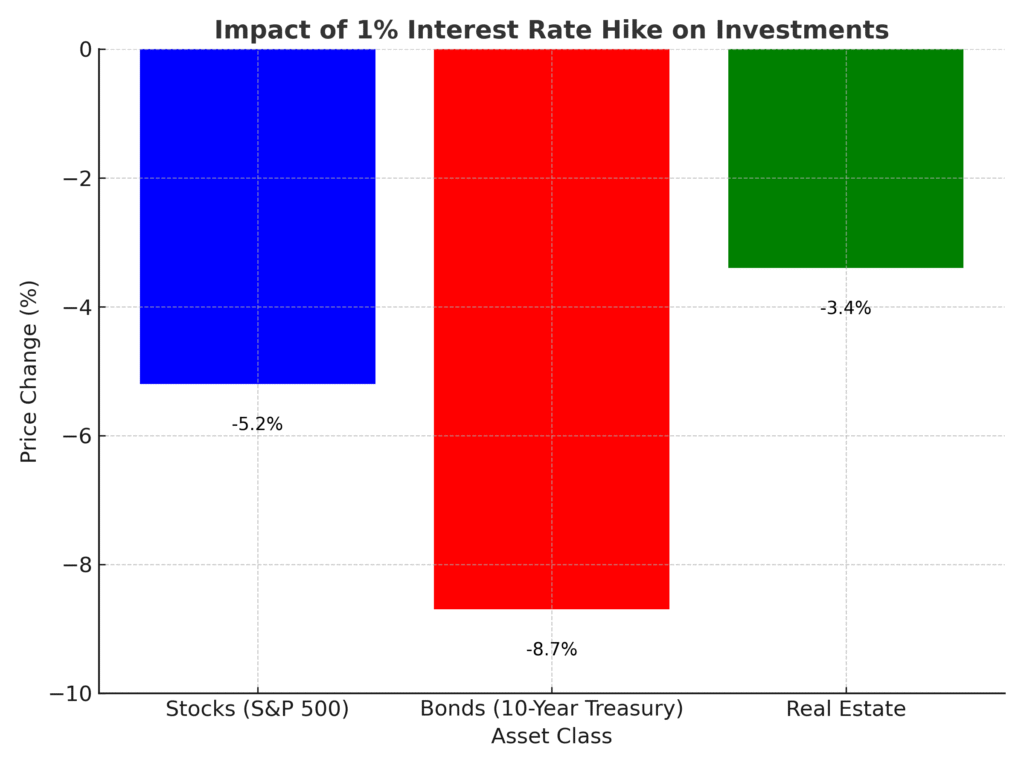
Interest rate changes significantly impact stock markets. Higher rates increase borrowing costs for companies, reducing profits and stock valuations. Historical data shows that a 1% rate hike typically leads to a 5.2% decline in the S&P 500 over six months, as seen in 2018. Conversely, low rates fuel equity rallies by encouraging investment. For example, the Fed’s near-zero rates in 2020–2021 drove a 30% S&P 500 surge. Growth sectors like technology are particularly sensitive to rate hikes due to their reliance on debt financing.
Bonds
Bond prices move inversely to interest rates. When rates rise, existing bonds with lower yields lose value, as newer bonds offer higher returns. A 1% rate hike in 2023 reduced 10-year Treasury bond prices by approximately 8.7%. Investors holding long-term bonds face higher risks during tightening cycles, while short-term bonds offer more stability.
Real Estate
Monetary policy affects real estate through mortgage rates. Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, reducing homebuyer demand and impacting real estate investment trusts (REITs). A 1% rate hike typically slows property price growth by 3–4%, as seen in 2022. Low-rate environments, like 2020, fuel real estate booms by making mortgages more affordable.
Currencies
Tight monetary policy strengthens a country’s currency by attracting foreign investment seeking higher yields. The U.S. dollar rallied 10% during the Fed’s 2022 tightening cycle, impacting global investors. A stronger currency can hurt exporters but benefits those holding dollar-denominated assets.
To visualize these effects, we’ve included an interactive chart below, showing the average impact of a 1% interest rate hike on key asset classes. If the chart isn’t visible, it displays a 5.2% drop in stocks (S&P 500), an 8.7% decline in 10-year Treasury bonds, and a 3.4% reduction in real estate prices.
Interactive Chart: Impact of 1% Interest Rate Hike on Investments
Description: The chart compares the percentage price change in stocks, bonds, and real estate after a 1% rate hike, based on historical averages.
Strategies for Investors
Navigating monetary policy requires strategic planning to protect and grow your portfolio. Here are five actionable tips, grounded in economic principles:
- Diversify Across Asset Classes: Spread investments across stocks, bonds, commodities, and real estate to mitigate risks from policy shifts. For example, commodities like gold often perform well during inflationary periods driven by loose policy.
- Adopt Bond Laddering: Invest in bonds with staggered maturities (e.g., 1, 3, 5 years) to reduce interest rate risk. This ensures regular cash flow and flexibility to reinvest at higher yields if rates rise.
- Prioritize Defensive Stocks: Sectors like utilities, healthcare, and consumer staples are less sensitive to rate hikes, offering stability during tightening cycles. For instance, utility stocks gained 3% during the 2018 rate hikes while tech fell 7%.
- Monitor Central Bank Signals: Stay informed by following Federal Reserve FOMC statements, ECB press conferences, or Bank of Japan reports. These signals can hint at upcoming rate changes or QE programs. Subscribe to our newsletter for real-time updates.
- Use Inflation-Hedged Assets: Consider Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) or ETFs like the iShares TIPS Bond ETF to guard against inflation spikes from loose monetary policy.
These strategies align with broader economic trends, as explored in our Global Economic Outlook 2025, and can help you navigate policy-driven volatility.
Case Studies: Monetary Policy in Action
To illustrate monetary policy’s real-world impact, let’s examine two pivotal examples:
- Federal Reserve’s 2008 Quantitative Easing: During the 2008 financial crisis, the Fed launched a $1.7 trillion QE program, buying bonds to inject liquidity. This stabilized markets, driving a 26% S&P 500 rally in 2009. Investors who shifted to equities early capitalized on the recovery, while those in bonds faced low yields due to suppressed rates.
- ECB’s Negative Interest Rates (2014–2019): The ECB adopted negative rates to stimulate the Eurozone economy, boosting bond prices but hurting savers. Investors in European equities saw modest gains, while real estate markets in cities like Berlin surged due to cheap borrowing.
These cases highlight the importance of adapting to policy shifts, whether you’re investing in U.S. markets or globally.
Global Perspective: Monetary Policy Beyond the U.S.
While the Federal Reserve dominates headlines, other central banks shape global markets. The ECB’s cautious tightening in 2023 contrasted with the Bank of Japan’s ultra-loose policy, impacting currency and equity markets differently. For example, Japan’s yen weakened 15% against the dollar in 2022, affecting global investors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for diversified portfolios, especially in 2025’s interconnected economy (see Global Economic Outlook 2025).
FAQ: Common Questions About Monetary Policy
- What is monetary policy? Actions by central banks to manage money supply and interest rates for economic stability.
- How does monetary policy affect stocks? Rate hikes reduce valuations; low rates spur growth.
- What’s the difference between monetary and fiscal policy? Monetary policy is set by central banks; fiscal policy involves government spending/taxes. Learn more in Fiscal Policy Explained.
- How can investors prepare for rate hikes? Diversify, use bond laddering, and focus on defensive stocks or TIPS.
- Why do central banks use QE? To inject liquidity during crises, stabilizing markets but risking asset bubbles
Monetary policy is a powerful force shaping your investments, from stock market swings to bond yield fluctuations. By understanding how central banks like the Federal Reserve, ECB, and Bank of Japan use interest rates, QE, and other tools, you can make informed decisions to protect and grow your wealth. Whether it’s diversifying your portfolio, laddering bonds, or monitoring policy signals, proactive strategies are key to thriving in any economic environment. Stay ahead with our Economic Insight series, and share this post on X to join the conversation!
